Iterators
Context:
Classes ValueTypes Interfaces Type Members
iterator-specification
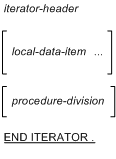 |
iterator-header
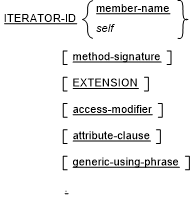 |
Example
Here we use an iterator-id paragraph GetEven to return the even numbers in the m-FibonacciArray
class-id Fibonacci.Class1 static.
data division.
working-storage section.
01 m-FibonacciArray binary-long occurs any static.
method-id FibEvens static.
procedure division.
set content of m-FibonacciArray to (1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144)
display "Even numbers in the Fibonacci sequence:"
perform varying evenNumber as binary-long through self::GetEven
display evenNumber
end-perform
goback.
end method.
iterator-id GetEven yielding res as binary-long static.
perform varying i as binary-long through m-FibonacciArray
if i b-and 1 = 0
set res to i
goback
end-if
end-perform
stop iterator *> stops the iterator explicitly
end iterator. *> end of method stops the iterator implicitly
end class.
The following is a similar example, but uses the self syntax to allow iteration directly through the current class (that is, the class in which the iterator appears).
class-id Fibonacci.Class2.
method-id main static (args as string occurs any).
try
declare max as binary-long = binary-long::Parse(args[0])
declare fibs = new Fibonacci(max)
perform varying i as binary-long through fibs
display i
end-perform
catch
display "Bad command line"
end-try
end method.
end class.
class-id Fibonacci.
01 MaxNumber binary-long.
method-id new (#max as binary-long).
set MaxNumber to #max
end method.
iterator-id self yielding res as binary-long.
set res to 1
exit iterator
declare frst as binary-long = 0
declare second as binary-long = 1
perform until exit
compute res = frst + second
if res > MaxNumber
stop iterator
end-if
move second to frst
move res to second
exit iterator
end-perform
end iterator.
end class.
See also the Iterators sample, which is available from Start > All Programs > Micro Focus Enterprise Developer > Samples > Visual COBOL Samples, under COBOL for .NET.
Further information
If you specify parameters in the iterator header, you must not include a procedure division header in the body of the iterator.
The STOP ITERATOR statement stops the iteration.
This statement is not needed if the next statement is END ITERATOR.