Overview
Welcome to the AcuServer file server, a client/server technology that provides remote file access services to ACUCOBOL-GT® applications running on UNIX and Windows TCP/IP-based networks.
With AcuServer, your applications gain:
- The ability to create and store data files on any UNIX, Windows NT, Windows 2000 to 2008 server equipped with AcuServer.
- Full function remote access from UNIX and Windows clients to all Vision, relative, sequential, and object files stored on an AcuServer server.
- Full record locking support of all Vision and relative files.
- Transparent access of remote and local files.
(Some applications that contain hard-coded paths to files must be modified to use the FILE_PREFIX or CODE_PREFIX environment variable, or to include the name of the file server in the path. See Accessing Remote Files for a discussion of name strategies.
AcuServer does not require that you recompile your existing programs. Programs compiled with any version of ACUCOBOL-GT can be executed by any later version of ACUCOBOL-GT. ACUCOBOL-GT runtimes are available for most UNIX and Windows platforms. Contact our customer service representative for a current list of supported platforms.
AcuServer can be combined with other extend technologies to provide access to data in networked, client/server, and distributed computing environments. It can be used with the ACUCOBOL-GT Web Runtime to provide access to data over the World Wide Web (with permission). It can be used with ACUCOBOL-GT's CGI technologies to provide Internet access to data through an HTML front end. And it can be combined with AcuConnect® to facilitate file distribution and optimize network performance in a distributed computing setting.
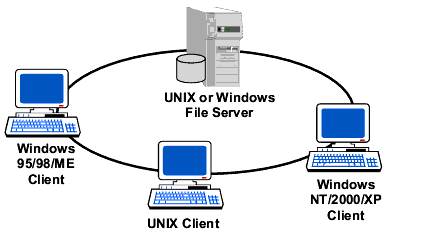
Pictured below is a simple AcuServer network. ACUCOBOL-GT applications running on UNIX and Windows client systems access and store data files on a common UNIX, Windows NT, Windows 2000 to 2008 file server running AcuServer. More complex networks might incorporate multiple AcuServer file servers supporting dozens of client machines running multiple applications.
Unless otherwise indicated, the references to Windows in this manual denote the following 32-bit versions of the Windows operating systems: Windows XP, Windows NT 4.0 or later, Windows 2000, Windows 2003; and the following 64-bit version of the Windows operating system: Windows Server 2003 and 2008 x64. When necessary specific version numbers are used (Windows 2000, Windows NT 4.0, and so on).