Features Added in Visual COBOL 2.2
COBOL copybook project types
You can use the COBOL Copybook and Remote COBOL Copybook project types to create project that hold several copybook files. In these projects you can only create new or add existing .cpy and .cbl files but files with the .cbl extension are treated as copybooks.
You can then add these projects as dependent projects to the build path of other projects that include the source files. Copybook projects are not compiled, thus saving processing time and resources.
COBOL Source Information (CSI)
COBOL Source Information (CSI) provides a quick and easy way of providing you with information about your program when you are working on it. You enter a query in the Quick Browse dialog box and CSI returns the results of the query in the Search view.
Compiler directives
The following Compiler directives are new:
- ACU-UNDERSCORE
- This directive treats underscores in COBOL words as hyphens.
- ILSHOWPERFORMOVERLAP
- This managed COBOL-only directive generates a warning when an overlapping PERFORM range is detected in the program.
- ILEXPONENTIATION
- This managed COBOL-only directive enables you to optimize exponential arithmetic operations by specifying the calculation method used.
- EXITPROGRAM
- This directive determines how the EXIT PROGRAM statement is executed.
The following Compiler directives have changed:
- CHANGE-MESSAGE
- The scope of this directive has been widened to allow you to change the severity of different types of error messages, not just syntax checking messages.
- DIALECT"RM"
- DIALECT"RM" now sets PERFORM-TYPE"RM". If you recompile an application that uses DIALECT"RM", the behavior may change for nested PERFORM statements. If that is the case, explicitly set PERFORM-TYPE"MF" after DIALECT"RM" to continue with the previous behavior.
- HIDE-MESSAGE
- The scope of this directive has been widened to allow you to hide different types of error messages, not just syntax checking messages.
- PRESERVECASE
- This directive now defaults to PRESERVECASE when compiling native COBOL; managed COBOL compilation already defaults to PRESERVECASE. This results in externally visible identifiers preserving their case instead of being converted to uppercase.
Consolidated copybook paths dialog box
You now set the paths for COBOL, IMS, and PL/I copybooks (where available for the project type) in a single Dependency Paths page of the project properties dialog box.
Consolidated Tracing Facility
The following changes have been made to the Consolidated Tracing Facility (CTF):
CTF for JVM COBOL applications
CTF tracing is now supported in JVM COBOL applications.
Emitters
A new emitter, JAVALOGGER, is available for JVM COBOL.
Emitter properties and variables
The following support has been added to existing emitters.
The following property has been added to the BINFILE emitter:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| RunUnitID | Controls whether the RunUnit information is included in the trace. |
Four new pseudo-variables for the FILE property have been added to the BINFILE and TEXTFILE emitters:
| pseudo-variable | Description |
|---|---|
| $(PLATFORM) | A platform specific constant, useful when two run-time systems are in the same process, and you require separate trace files |
| $(RUNUNIT) | A unique number that represents the managed RunUnit ID |
| $(RUNUNIT_SESSIONNAME) | The session name passed to the managed RunUnit |
| $(RUNUNIT_GUID) | The globally unique identifier associated with the managed RunUnit |
Documentation
The following guide is now available, among other updates to the product help for this release:
- Object-Oriented Programming
- A guide that provides a basic introduction to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) for COBOL developers, An Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming for COBOL Developers, is now available from the Product Documentation section on the OpenText Support and Services Documentation Web site for Micro Focus products.
Eclipse 3.8
Visual COBOL is shipped with Eclipse 3.8, and can also be installed in existing instances of Eclipse 3.7 and 3.8.
Enhanced Enterprise Server integration with the IDE
This release provides the following enhancements:
- Creating a server from a template directly from the Server Explorer window.
- Automatically starting the associated server and enabling dynamic debugging for it when you start debugging.
- Showing the spool and the catalog of the associated server from the context menu for the project in COBOL Explorer.
- Debugging applications using a temporary server when the project has no association with any of the existing enterprise servers.
File Handling
New features include:
- The DATEDIFF function as part of the DFSORT emulation. There are some limitations of its use in Visual COBOL.
- Converting and editing Vision and RM/COBOL indexed data files using the Data File tools.
- Access to data files (either sequential or indexed) through AcuServer.
- Access to Vision and RM/COBOL indexed data files through Enterprise Server.
IMTK
- Improved IMTK usability
- The Interface Mapping Toolkit (IMTK) perspective and associated views and commands have been removed and the functionality integrated into the COBOL perspective.
- EJB transactions
- Visual COBOL now supports EJB services that execute as a transaction.
Java Web services support
Visual COBOL supports the development, compilation, debugging, and deployment of JVM COBOL web archives to JVM servlet APIs and common Java Enterprise Edition (JEE) application servers.
JVM COBOL Web services support
Support for calling COBOL programs from JSPs and servlets has been expanded to offer more COBOL features, improved IDE tools, and more runtime support.
Mainframe snippets
A number of code snippets for inserting EXEC CICS and EXEC DLI statements in the code are now available for Mainframe Subsystem applications. You can insert code snippets from the context menu in the editor or by pressing Control + Space and selecting a keyword. You can modify the keywords for the mainframe snippets in the IDE from Window > Preferences > Micro Focus > COBOL > Editor > Templates.
Managed COBOL
- Named and optional parameters
- Two new types of parameter have been introduced for use during method invocation:
- Named parameters
- As part of the invocation expression, you can define a value for a parameter named in the method definition. The named argument must be specified after any positional arguments, and must not correspond to any of those preceding arguments.
- Optional parameters
- Optional parameters are parameters defined with a default value in the procedure division header of the invoked method. If none of the arguments passed in during invocation correspond to this parameter, the default value is used in the method; if an argument does correspond, the value that was passed in is used.
- Delegates and events
-
A number of new features have been added that relate to delegates and events:
Note: Some of these features were also available in previous versions of Visual COBOL.- The ATTACH and DETACH statements
- Use these statements to attach or detach a delegate, method group or an anonymous method to or from an event.
- The RUN statement
- Use this statement to invoke a delegate once it has been created.
- Combining delegates
- Use the '+' operator to add a method group, anonymous method or another delegate to a delegate, and use the '-' operator to remove a method or another delegate from a delegate.
- Method groups conversions
- Use the METHOD keyword to specify a compatible method from a method group, and convert it to a delegate.
Problems view
The Problems view now has a 'Program' column that displays the name of the program in which the problem occurred. Click this column heading to sort the errors by program.
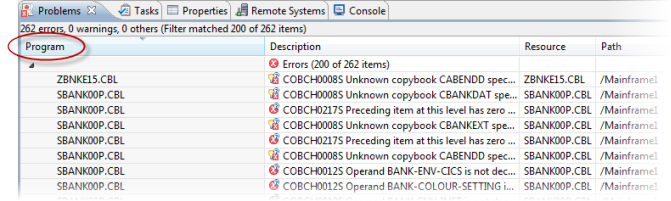
If the column is not present in the view by default, you can add it through the Configure Columns dialog box in the View Menu.
Quickfix for missing copybooks
When paths containing copybooks are added to a project, they are not automatically added to the copypath. This can cause confusion when a copybook is in the project but the program is not compiling. The Eclipse Quickfix feature now hints how to resolve the problem, and offers a solution (which is to add the path onto the copypath).
SQL
- Eclipse IDE
- SQL tooling has been integrated into the Eclipse IDE:
- HCO for SQL Server tools
- OpenESQL Assistant
- Options for the level of background parsing for DB2, XDB, and OpenESQL statements
- EXEC SQL GET DIAGNOSTICS Statement
- Enables you to get diagnostic information for the last OpenESQL statement executed.
- External Compiler Modules (ECM)
- ECM support has been expanded and includes OpenESQL, HCO for DB2 LUW, and XDB.
- OPTION compiler directive option
- New parameters have been added to handle additional host variable types.
Viewing copybook dependencies
By expanding a source file node in COBOL Explorer, you can see a list of all copybooks referenced in the source code, and nested within them any other copybooks referenced by those copybooks.
You can also use the Copybook Dependency view to show where in the source file's structure the COPY statements appear, and which copybooks they reference.
Click a copybook reference in the Copybook Dependency view to open the file containing the associated COPY statement at the appropriate line.
Double-click a copybook reference in COBOL Explorer or Copybook Dependency view to open the copybook file.
XML Extensions
You can now use XML Extensions in your managed COBOL projects.