COBOL Views
The following shows examples of views that are available by default for the COBOL perspective.
COBOL Editor
The COBOL editor provides numerous features to help you write your code such as:
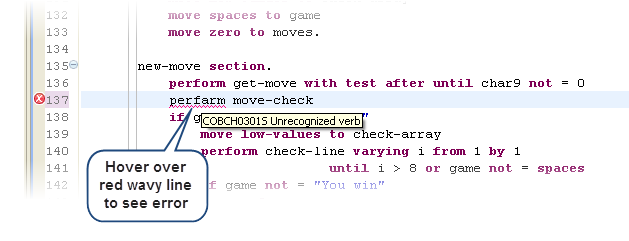
- Background parsing underlines errors as you type, while hovering over the item gives information on the error.
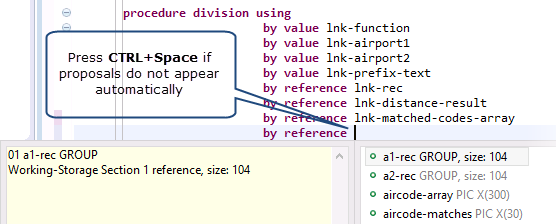
- Content Assist provides context sensitive proposals for typing COBOL code in the editor.
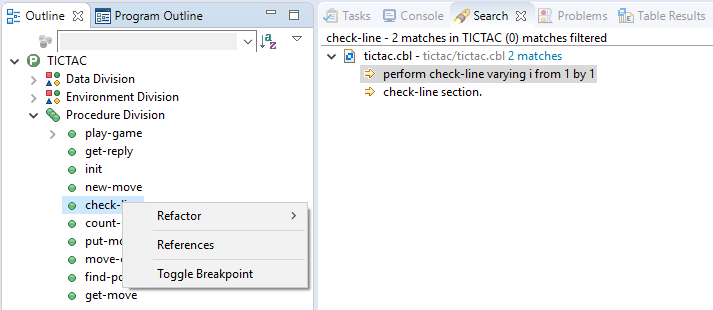
- You can search for references to any variable in your code. In the Outline view, right-click the variable, and then click
Reference.
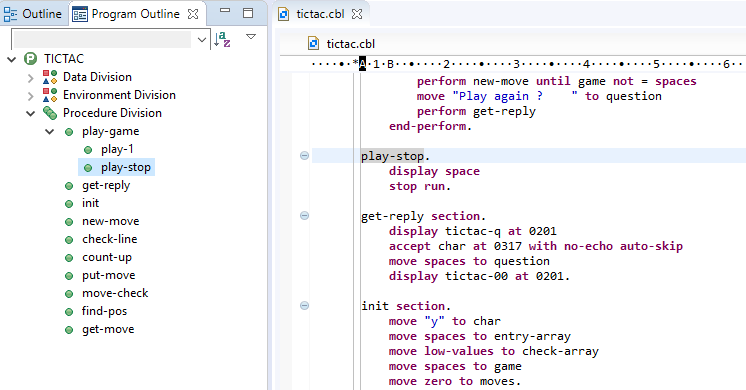
- The Outline view shows the structure of the file you are editing. This view enables you to navigate around the file. For
example, if you want to go to a particular COBOL section or a data item in the Editor view, just click on it in the Outline
view.
- In the Outline and Program Outline views you can open the Type Hierarchy and Call Hierarchy view for JVM COBOL. Right-click the item and then click Open Type Hierarchy or Open Call Hierarchy as required.
- You can use block selection to move blocks of text. Press
Alt+Shift+A to switch to block selection mode, then click and drag to select.

- By using the COBOL Copy View you can view copybooks inline, enabling you to see the effects of COPY … REPLACING, as in the following example. You can open COBOL Copy View when working in the COBOL editor by pressing F4.
COBOL Explorer
The COBOL Explorer view includes the following features to help you manage your projects:
- For COBOL Project, Remote Project, and Mainframe Project types, COBOL Explorer adds category folders that automatically group together your project's COBOL programs, copybooks, and output files. (These folders are not physical folders on the disk, but effectively headings for certain file types.)
- You can filter the tree view by typing strings in the COBOL Explorer search filter. Wildcard characters can be used in the search strings. The question mark character (?) matches a single character. An asterisk (*) matches a number of characters. The search field can store the previous 10 search strings.
- By default, the COBOL Explorer displays COBOL JVM projects in package presentation. This is where COBOL JVM is organized in
the same way as a Java package. So that Java classes, interfaces, and types are displayed in their namespaces. For example,
the package com.microfocus.example is displayed as:
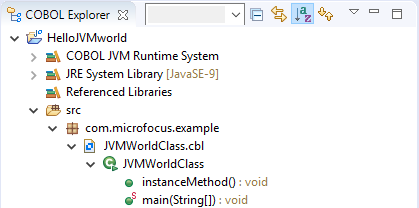
To change the presentation to display COBOL categories, click
 (View Menu), and then click
. The same class file is now displayed as:
(View Menu), and then click
. The same class file is now displayed as: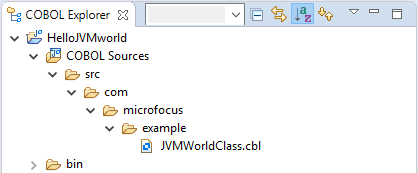
- You can open the Call Hierarchy view for JVM COBOL projects, folders, programs. To open the view, right-click the item in the COBOL Explorer, and then click Open Call Hierarchy. Alternatively, press Ctrl+Alt+H. The view enables you to see the callers and callees hierarchy for the selected JVM COBOL member.
- You can open the Type Hierarchy view for JVM COBOL type. To open the view, right-click the type in the COBOL Explorer, and then click Open Type Hierarchy. Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+H. The view enables you to see classes, subclasses and members and their supertypes, or their subtypes.
- To simplify navigation around your project, you can hide some files that are part of the project, such as the
.cobolBuild,
.cobolProj, and
.project files, and the
.settings folder and its content in JVM projects. In the COBOL Explorer, click
 and then click
Customize View and choose from the options.
and then click
Customize View and choose from the options.
- Filters
- Choose types of content to hide in COBOL Explorer:
Option Description .*resources Any files of type .* such as .cobolBuild, .cobolProj. COBOL Copybook projects Any COBOL Copybook projects. COBOL JVM output folders Closed projects Resources in closed projects never display, but you can choose to hide all closed project icons  too.
too.
Derived COBOL programs Programs that have been generated by COBOL preprocessors. Empty categories COBOL Projects that do not contain COBOL program or copybook files. Empty folders inside categories Folders mapped to the COBOL Programs and Copybooks that contain no COBOL program or copybook files. Empty folders outside categories Folders not mapped to the COBOL Programs and Copybooks that contain no COBOL program or copybook files. Empty packages All empty packages are removed from the view. Empty parent packages All empty parent packages are removed from the view. Internal Micro Focus project Internal Micro Focus projects. Non-Micro Focus projects Non-Micro Focus projects. Non-public members All non-public members are removed from the view. PL/I Include projects PL/I include projects. RSE Internal projects Projects generated by the RSE plug-in. Synthetic members All synthetic members, such as $0, are removed from the view. - Content
- Choose types of content to show in COBOL Explorer:
Option Description Working Sets Working sets are subsets of workspace resources you can choose to show or perform options on. To define a working set, click Project > Build Working Set > Select Working Set > New. COBOL Elements Non-resource types that are COBOL-specific: - x
- Category folders, including those for COBOL programs and copybooks
- Icons for the different types of COBOL files.
- Overlays for build errors and warnings
- Some context menu items
COBOL JVM Package Presentation By default, this option is checked. This option, when combined with the , displays COBOL JVM projects in package presentation view. If this is not checked then the content of the COBOL JVM project is displayed as they are in the file system. Resources COBOL projects, COBOL programs and copybooks. Has effect only if the COBOL Elements option is unchecked.
- COBOL Explorer helps you fix problems by using icons to identify files and containers that cause build errors and warnings.
- A file that generates a warning, and any containing folders and categories, is marked with a yellow warning sign. For example:
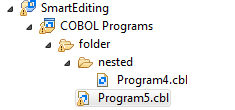
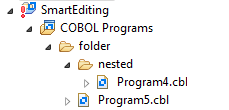
- A file that causes an error, and any containing folders and categories, is marked with a cross. In this example the icons
indicate the most severe problem is the error caused by Program4.cbl, and the folders are marked with error icons despite
Program5.cbl
generating a warning:
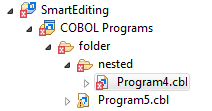
- A project that suffers from a dependency error is marked with a red exclamation point; its contents remain unmarked. In this
example the project depends on another project that is closed, causing a build path problem:
- A file that generates a warning, and any containing folders and categories, is marked with a yellow warning sign. For example: