The Repository Paragraph
General Format
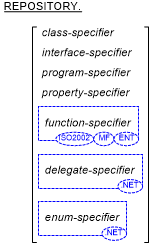
where class-specifier is:

where interface-specifier is:
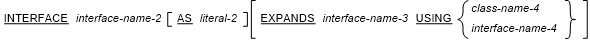
where program-specifier is:
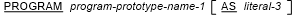
where property-specifier is:
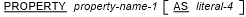
where function-specifier is:
Format 1 (user-defined)
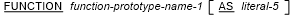
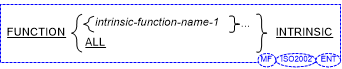
Function 2 (intrinsic)
where delegate-specifier is:

where enum-specifier is:

Directives
- In addition to the Compiler directives which provide flagging and modify the reserved word list, the following directives
may impact either the syntax or the semantics described in this section.
- REPOSITORY - Creates a repository file or requests that the program being compiled is checked against the repository file.
- RDFPATH - specifies the location of the library for the repository files.
- ACTUAL-PARAMS - specifies the parameters to be used in the creation of a class or interface from a parameterized class or interface
Note: None of these directives are applicable to .NET COBOL.
Syntax Rules
- If any class-name-1, delegate-name-1, enum-name-1, interface-name-2, function-prototype-name-2, intrinsic-function-name-1, property-name-1 or program-prototype-name-1 is specified more than once in the Repository paragraph, all the specifications for that name must be identical.
- Literal-1, literal-2, literal-3, literal-4, literal-5, literal-6 and literal-7 must be nonnumeric literals and must not be figurative constants.
- If the CLASS clause is specified, class-name-2, class-name-3, and interface-name-1 must be:
- Parameters of a containing class definition or interface definition; or
- Defined in the same Repository paragraph where class-name-1 is defined.
- If class-name-1 is specified in the USING phrase of the Class-ID paragraph of a class definition containing this Repository paragraph or in the USING phrase of the Interface-ID paragraph of an interface definition containing this Repository paragraph, the EXPANDS phrase must not be specified.
- If the INTERFACE clause is specified, class-name-4, interface-name-3 and interface-name-4 must be:
- Parameters of a containing class definition or interface definition; or
- Defined in the same repository paragraph where interface-name-2 is defined.
- If interface-name-2 is specified in the USING phrase of the Class-ID paragraph of a class definition containing this Repository paragraph or in the USING phrase of the Interface-ID paragraph of an interface definition containing this Repository paragraph, the EXPANDS phrase must not be specified.
- Either program-prototype-name-1 must be the name of a program prototype or a program definition specified previously in this
compilation group or:
- If literal-3 is not specified, there must be information in the external repository for the program program-prototype-name-1,
- If literal-3 is specified, there must be information in the external repository for the program literal-3.
- Either function-prototype-name-1 must be the name of a function prototype or a function definition specified previously in
this compilation group or:
- If literal-5 is not specified, there must be information in the external repository for the function function-prototype-name-1,
- If literal-5 is specified, there must be information in the external repository for the function literal-5.
 Intrinsic-function-name-1:
Intrinsic-function-name-1:
- Must be the name of a supported COBOL intrinsic function.
- Not specified as a user-defined word within the scope of this Repository paragraph.
- If specifying the same function more than once in the REPOSITORY paragraph, all specifications for that name shall be identical.
- May be specified as a function-identifier without being preceded by the keyword FUNCTION within the scope of the containing environment division.

 If ALL is specified in the intrinsic format of the function-specifier, none of the names of the intrinsic functions can be
specified as a user-defined word within the scope of the Repository paragraph.
If ALL is specified in the intrinsic format of the function-specifier, none of the names of the intrinsic functions can be
specified as a user-defined word within the scope of the Repository paragraph.
- If the specified class-name-1 is the name of the class definition in which this Repository paragraph is specified, references to class-name-1 are to that class definition and this class-specifier is ignored.
- If the specified interface-name-2 is the name of the interface definition in which this Repository paragraph is specified, references to interface-name-2 are to that interface definition and this interface-specifier is ignored.
- If the specified program-prototype-name-1 is the name of the program definition in which this Repository paragraph is specified or the name of a containing program, references to program-prototype-name-1 are to the named program definition and this program-specifier is ignored.
- If the specified function-prototype-name-1 is the name of the function definition in which this Repository paragraph is specified, references to function-prototype-name-1 are to that function definition and this function-specifier is ignored.
 If the specified delegate-name-1 is the name of the delegate definition in which this Repository paragraph is specified, references
to delegate-name-1 are to that delegate definition and this delegate-specifier is ignored.
If the specified delegate-name-1 is the name of the delegate definition in which this Repository paragraph is specified, references
to delegate-name-1 are to that delegate definition and this delegate-specifier is ignored.

 If the specified enum-name-1 is the name of the enumeration definition in which this Repository paragraph is specified, references
to enum-name-1 are to that enumeration definition and this enum-specifier is ignored.
If the specified enum-name-1 is the name of the enumeration definition in which this Repository paragraph is specified, references
to enum-name-1 are to that enumeration definition and this enum-specifier is ignored.
- If the CLASS clause is specified:
- If literal-1 is specified, there must be information in the external repository for the class literal-1.
- If literal-1 is not specified, there must be information in the external repository for the class class-name-1.
- If the INTERFACE clause is specified:
- If literal-2 is specified, there must be information in the external repository for the interface literal-2.
- If literal-2 is not specified, there must be information in the external repository for the interface interface-name-2.
- If the PROPERTY clause is specified:
- If literal-4 is specified, there must be information in the external repository for the property literal-4 that is part of one of the classes or interfaces that are declared in this Repository paragraph.
- If literal-4 is not specified, there must be information in the external repository for the property property-name-1 that is part of one of the classes or interfaces that are declared in this Repository paragraph.
 If the DELEGATE clause is specified:
If the DELEGATE clause is specified:
- If literal-6 is specified, there must be information in the external repository for the delegate definition literal-6.
- If literal-6 is not specified, there must be information in the external repository for the delegate definition literal-6.

 If the ENUM clause is specified:
If the ENUM clause is specified:
- If literal-7 is specified, there must be information in the external repository for the enumeration definition literal-7.
- If literal-7 is not specified, there must be information in the external repository for the enumeration definition literal-7.
General Rules
- Class-name-1 is the name of a class that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
- If the AS phrase is specified, literal-1, literal-2, literal-3, literal-5 or literal-6 is the name by which the class, interface, program, function or delegate respectively, is known to the operating environment. Literal-4 is the name known to the operating environment for a method that implements the named property. The AS phrase is required when the name of a class, interface, property, function or delegate does not follow the rules for formation of a user-defined word or when the name is case specific.
- Class-name-3 and interface-name-1 are actual parameters for the parameterized class referenced by class-name-2.
- Class-name-4 and interface-name-4 are actual parameters for the parameterized interface referenced by interface-name-3.
- If the EXPANDS phrase is specified in a class-specifier, a class class-name-1 is created from the parameterized class class-name-2.
The number of parameters in the USING phrase of the EXPANDS phrase of the class-specifier must be the same as the number of
parameters in the USING phrase of the CLASS-ID paragraph of class-name-2. The interface for class-name-1 is the interface
specified for class-name-2 with the parameters of class-name-2 replaced by the parameters specified in the class-specifier.
The class class-name-1 is created from the parameterized class class-name-2 by replacing each specification of the formal parameter by the corresponding actual parameter. This replacement is done after the processing of COPY and REPLACE statements.
- The compiler uses the information specified for class-name-1 together with the external repository to determine the details of the class that is to be used. The repository information for the class must be in a file whose name is the externalized name of the class with the extension rdf. If the RDFPATH directive is specified, the file must be in the specified directory; otherwise, the file must be in the local directory where the .int and .idy files will be created.
- Interface-name-2 is the name of an interface that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
- If the EXPANDS phrase is specified in an interface-specifier, an interface interface-name-2 is created from the parameterized
interface interface-name-3. The number of parameters in the USING phrase of the EXPANDS phrase of the interface-specifier
must be the same as the number of parameters in the USING phrase of the INTERFACE-ID paragraph of interface-name-3. The interface
for interface-name-2 is the interface specified for interface-name-3 with the parameters of interface-name-3 replaced by the
parameters specified in the interface-specifier.
The interface interface-name-2 is created from the parameterized interface interface-name-3 by replacing each specification of the formal parameter by the corresponding actual parameter. This replacement is done after the processing of COPY and REPLACE statements.
- The compiler uses the information specified for interface-name-2 together with the external repository to determine the details of the interface that is to be used. The repository information for the interface must be in a file whose name is the externalized name of the interface with the extension rdf. If the RDFPATH directive is specified, the file must be in the specified directory; otherwise, the file must be in the local directory where the .int and .idy files will be created.
- Property-name-1 is the name of an object property that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
- Program-prototype-name-1 is the name of a program prototype that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
 Delegate-name-1 is the name of a delegate definition that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
Delegate-name-1 is the name of a delegate definition that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
- Format 2 of the function-specifier is documentary only.

 If ALL is specified in the intrinsic format of the function-specifier, it is as if each of the intrinsic-function-names defined
in the topic
Intrinsic Functions were specified.
If ALL is specified in the intrinsic format of the function-specifier, it is as if each of the intrinsic-function-names defined
in the topic
Intrinsic Functions were specified.

 If ALL is specified, you shall not specify any intrinsic function name as a user-defined word, within the scope of this REPOSITORY
paragraph.
If ALL is specified, you shall not specify any intrinsic function name as a user-defined word, within the scope of this REPOSITORY
paragraph.

 Enum-name-1 is the name of an enumeration definition that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
Enum-name-1 is the name of an enumeration definition that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
- If a prototype definition or a program definition for program-prototype-name-1 is specified previously in this compilation group, that definition is used to determine the details for activating the program identified by program-prototoype-name-1. Otherwise, the external repository is used to determine the details for activating the program with the externalized name program-prototype-name-1 and that program is activated when program-prototype-name-1 is referenced.
- Function-prototype-name-1 is the name of a function prototype that may be used throughout the scope of the containing Environment Division.
- If a prototype definition or a function definition for function-prototype-name-1 is specified previously in this compilation group, that definition is used to determine the details for activating the function identified by function-prototoype-name-1. Otherwise, the external repository is used to determine the details for activating the function with the externalized name function-prototype-name-1 and that function is activated when function-prototype-name-1 is referenced.